Communication Networks (7)
Pure P2P architecture
- no always-on server
- arbitrary end systems directly communicate
- peers are intermittently connected and change IP addresses
File distribution: client-server vs P2P
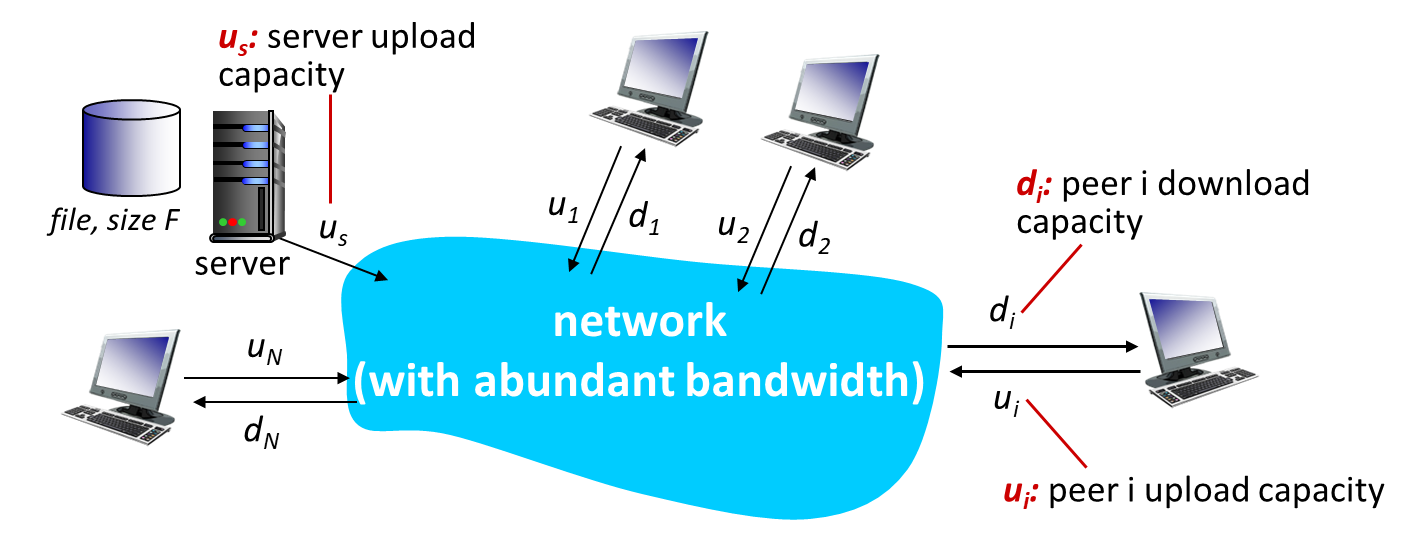
client-server model
Time to distribute to clients using client-server approach
Time to distribute to clients using P2P approach
P2P file distribution: BitTorrent
- File divided into 256Kb chunks
- Peers in torrent send/receive file chunks
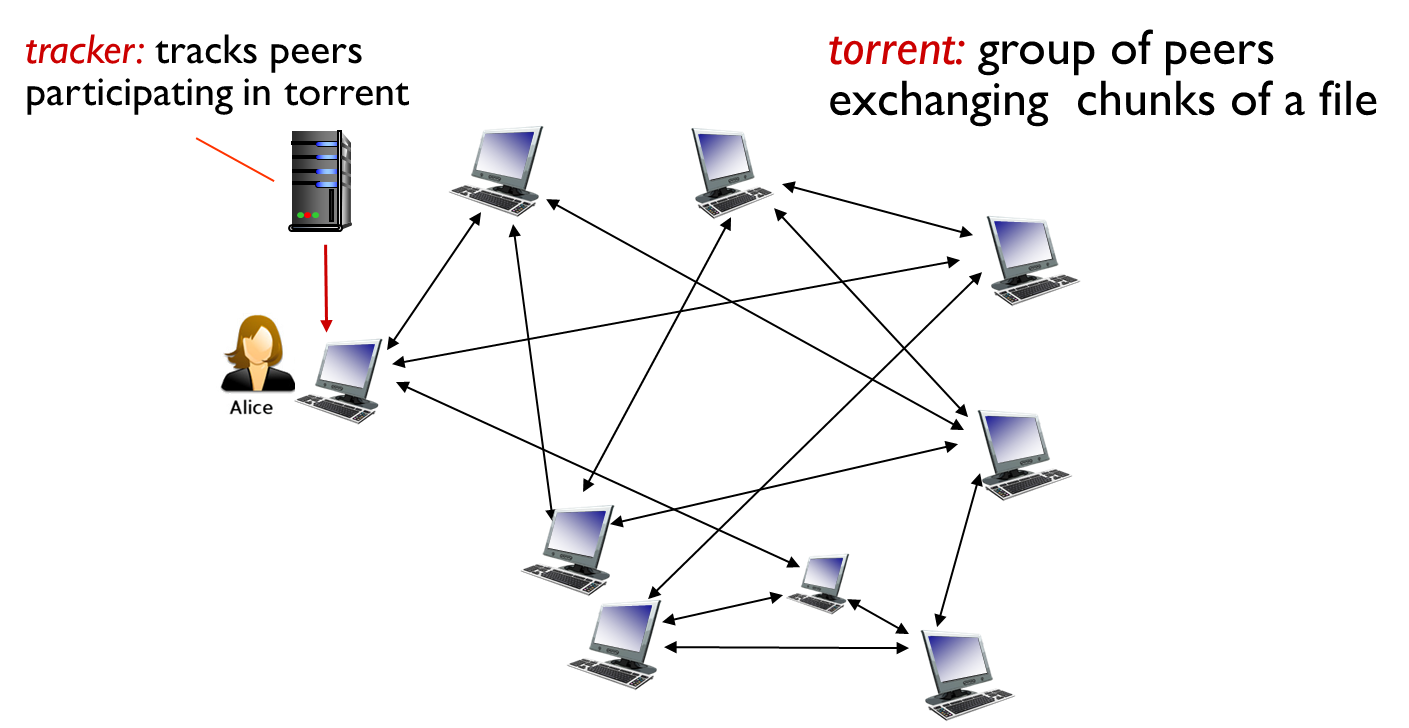

peer joining torrent:
- has no chunks, accumulate them over time from other peers.
- registers with tracker to get list of peers, connects to subset of peers (“neighbors”)
requesting chunks:
- different peers have different subsets of file chunks
- periodically, asks each peer for list of chunks that they have
- requests missing chunks from peers, rarest first
sending chunks: tit-for-tat
- sends chunks to those four peers currently sending her chunks at highest rate
- re-evaluate top 4 every 10 secs
- other peers are choked by Alice (do not receive chunks from her)
- every 30 secs: randomly select another peer, starts sending chunks
- newly chosen peer may join top 4 (and unchoke them)
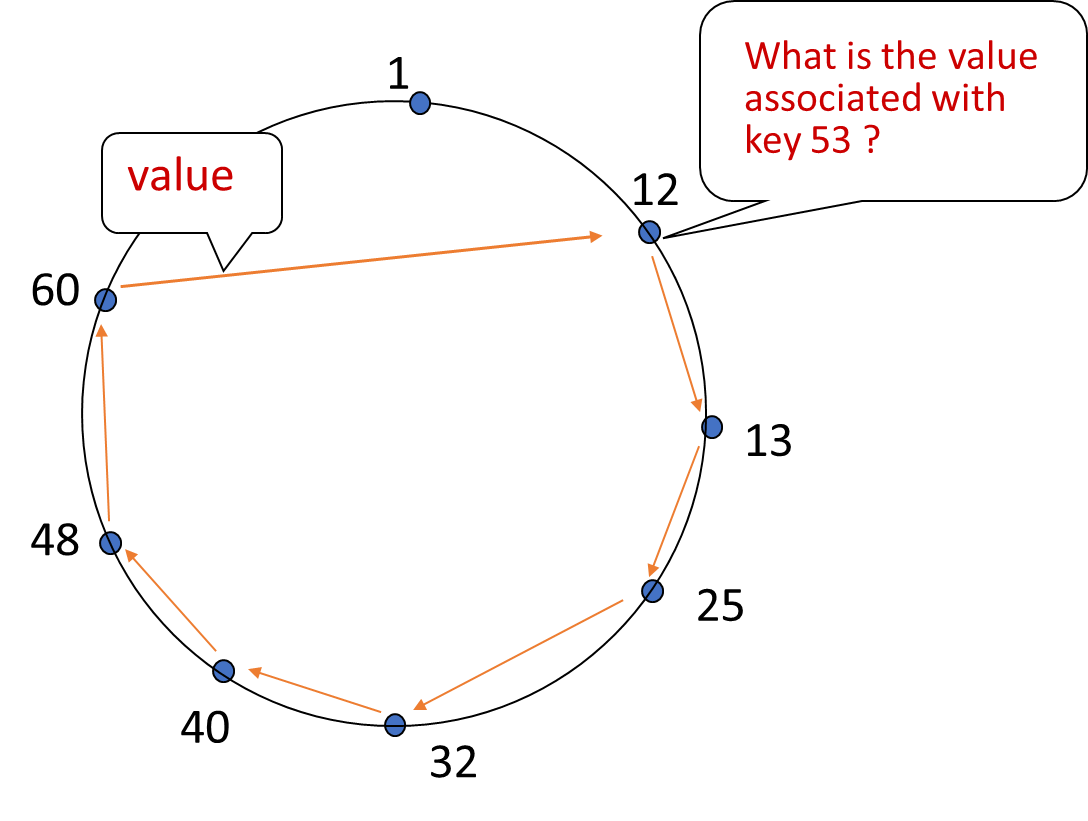
Distributed Hash Table (DHT)
Compared to simple Database, use Hash Table: key = hash(original key)
| Original | Key | Key Value |
|---|---|---|
| John Washington | 8962458 | 132-54-3570 |
| Diana Louise Jones | 7800356 | 761-55-3791 |
| … | … | … |
- Evenly distribute
(key, value)over pairs - Any peer can query database with a key
- Each peer only knows about a small number of other peers
- small number of messages exchanged among peers
Assign key-value pairs to peers
rule: assign key-value pair to the peer that has the closest ID (the immediate successor).
e.g., ID space
suppose 8 peers:
- If key = 51, then assigned to peer 60
- If key = 60, then assigned to peer 60
- If key = 61, then assigned to peer 1
{: .prompt-tip }
Silly Strawman Circular DHT
each peer only aware of immediate successor and predecessor.
_ _
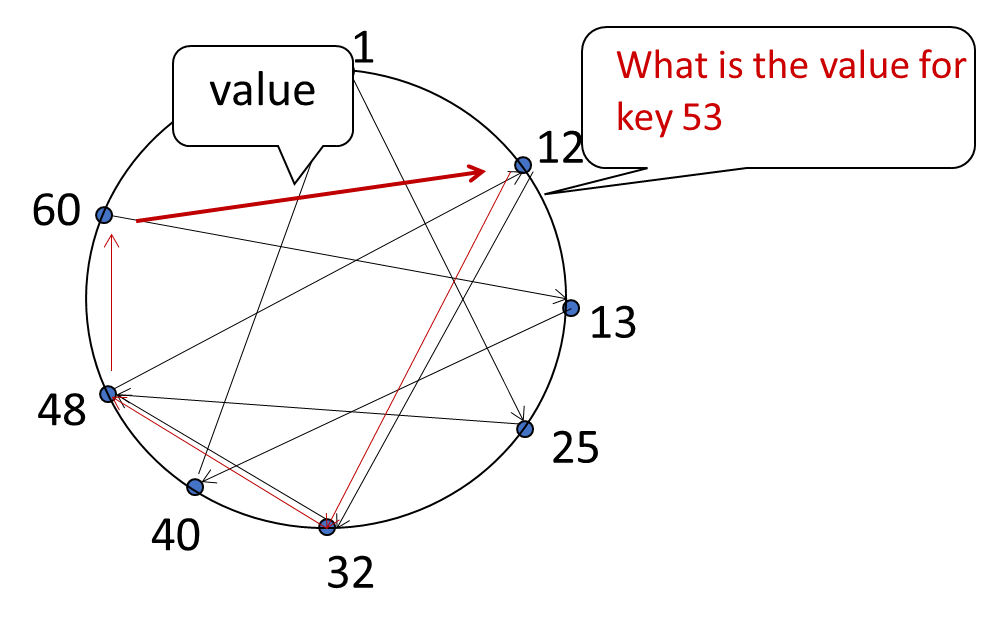
Circular DHT with shortcuts (Chord)
_ _
Peer churn
- peers may come and go (churn)
- each peer knows address of its two successors
- each peer periodically pings its two successors to check aliveness
- if immediate uccessor leaves, choose next successor as new immediate successor
- and ask for the successors of its new immediate successor
Video Streaming and CDNs
- CBR: (constant bit rate): video encoding rate fixed
- VBR: (variable bit rate): video encoding rate changes as amount of spatial, temporal coding changes
- examples:
- MPEG 1 (CD-ROM) 1.5 Mbps
- MPEG2 (DVD) 3-6 Mbps
- MPEG4 (often used in Internet, < 1 Mbps)
Streaming multimedia: DASH
DASH: Dynamic, Adaptive Streaming over HTTP
- divides video file into multiple chunks
- each chunk stored, encoded at different rates
- manifest file: provides URLs for different chunks
- client requests chunks according to server-to-client bandwidth.
Content distribution networks (CDN)
- To stream content to hundreds of thousands of simultaneous users.
- Store/serve multiple copies of videos at multiple geographically distributed sites (CDN)

Communication Networks (7)
https://yzzzf.xyz/2024/02/18/communication-networks-7/