Communication Networks (6)
Web caches (proxy server)
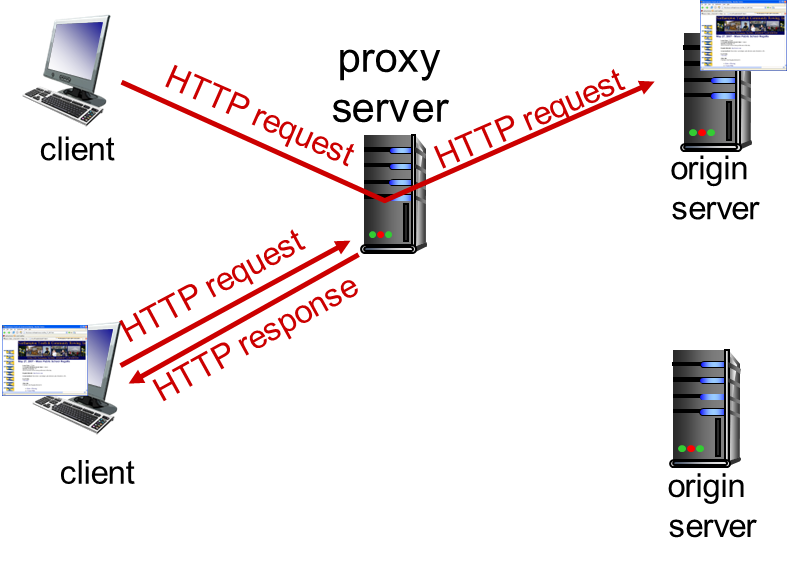
- browser sends all HTTP requests to cache
- object in cache: cache returns object
- else cache requests object from origin server, then returns object to client
Conditional GET
- send HTTP request with
If-modified-since: <date> - server response
HTTP/1.0 304 Not Modifiedif data not modified ever since - server response
HTTP/1.0 200 OK <data>otherwise
Chapter 2
Electronic mail
major components:
- user agents
- mail servers
- SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
Electronic Mail: SMTP [RFC 2821]
SMTP: protocol for exchanging email messages
- use TCP, port 25
- direct transfer
- three phases of transfer
- handshaking (greeting)
- transfer of messages
- closure
- command/response interaction like HTTP
- commands: ASCII text (7-bit)
- response: status code and phrase
Sample SMTP interaction
S: 220 hamburger.edu
C: HELO crepes.fr
S: 250 Hello crepes.fr, pleased to meet you
C: MAIL FROM: <alice@crepes.fr>
S: 250 alice@crepes.fr... Sender ok
C: RCPT TO: <bob@hamburger.edu>
S: 250 bob@hamburger.edu ... Recipient ok
C: DATA
S: 354 Enter mail, end with "." on a line by itself
C: Do you like ketchup?
C: How about pickles?
C: .
S: 250 Message accepted for delivery
C: QUIT
S: 221 hamburger.edu closing connection(end with CRLF.CRLF)
Mail message format
RFC 822: standard for text message format
- header lines, e.g.,
To:
From:
Subject:
(different from SMTP MAIL FROM) - Body: the “message” (ASCII characters only)
Mail access protocols
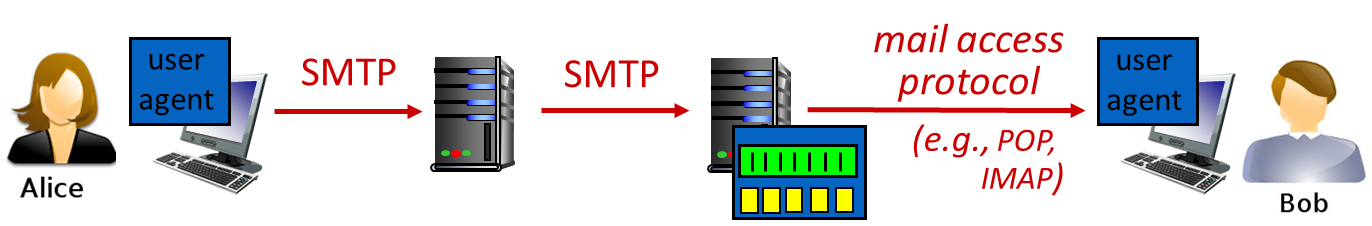
mail access protocol: retrieval from server
| protocol | description |
|---|---|
| POP | Post Office Protocol [RFC 1939]: authorization, download |
| IMAP | Internet Mail Access Protocol [RFC 1730]: more features, including manipulation of stored messages on server |
| HTTP | gmail, Hotmail, Yahoo! Mail, etc. |
DNS: domain name system
Domain Name System:
- distributed database (in hierarchy of name servers)
- application-layer protocol: hosts, name servers communicate to resolve names (address/name translation)
steps:
- client wants IP for
www.amazon.com; 1st approximation: - client queries root server to find com DNS server
- client queries
.comDNS server to getamazon.comDNS server - client queries
amazon.comDNS server to get IP address forwww.amazon.com
DNS name servers
Top-level domain (TLD) servers:
com,org,net,edu, …- top-level country domains:
uk,fr, …
Authoritative DNS servers:
- organization’s named hosts
- maintained by organization or service provider
Local DNS name server (cached)
- does not strictly belong to hierarchy
- each ISP has one
DNS name resolution example

Diterated query
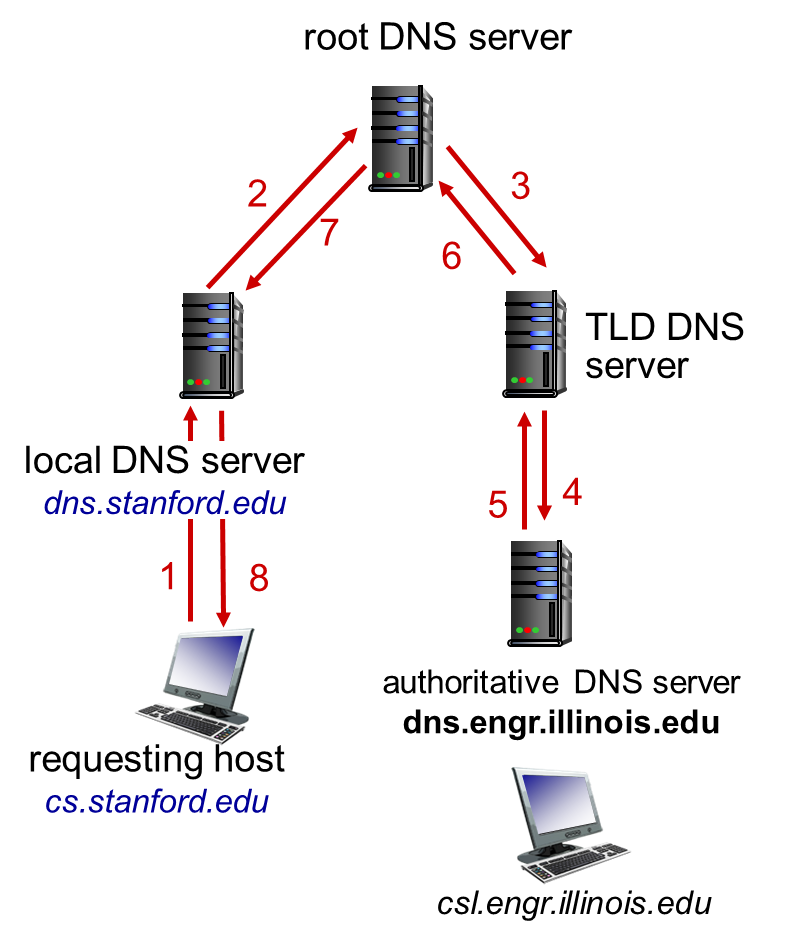
Name server caches mappings untiel expired (time of TTL)
DNS records
Distributed database storing resource records (RR).
RR Format: (name, value, type, ttl)
| type | name | value |
|---|---|---|
| A | hostname | IP address |
| NS | domain | hostname of authoritative name server for this domain |
| CNAME | alias name | is canonical(real) name |
| MX | hostname | mail server |
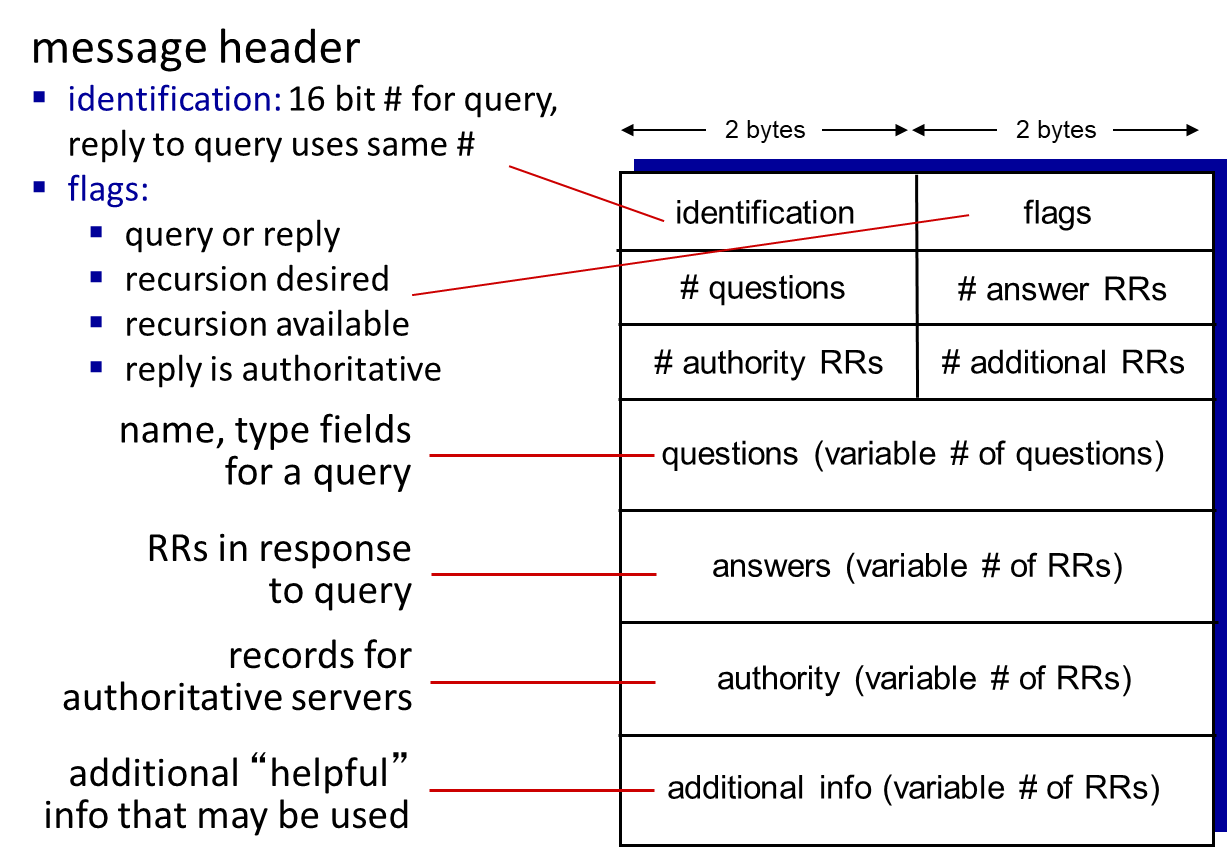
DNS protocol
Communication Networks (6)
https://yzzzf.xyz/2024/02/18/communication-networks-6/