Communication Networks (11)
TCP reliable data transfer
TCP ACK generation
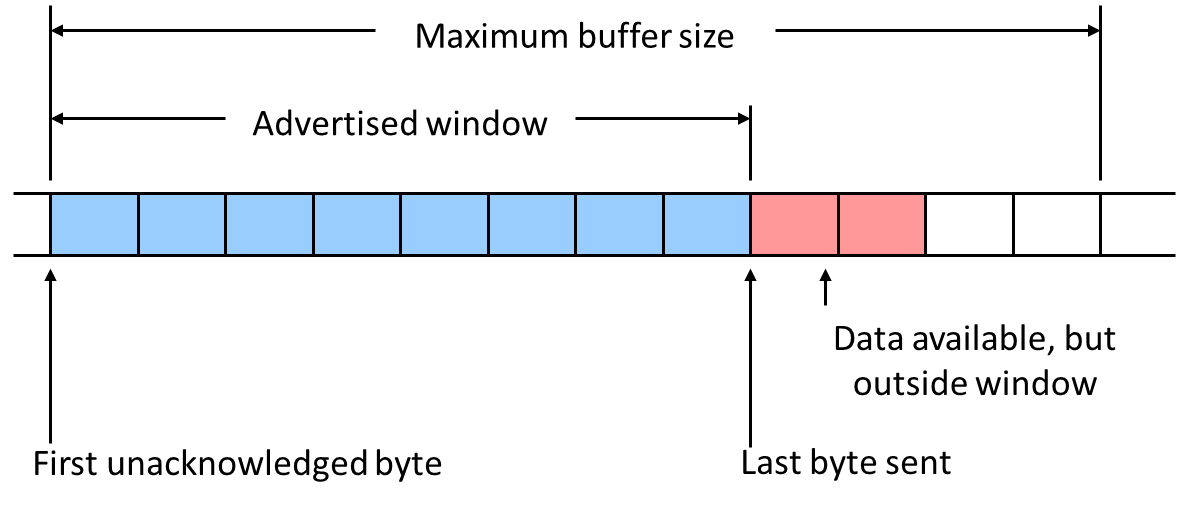

Arrival of in-order segment with expected seq #. One other segment has ACK pending | Immediately send single cumulative ACK, ACKing both in-order segments
Arrival of out-of-order segment higher-than-expect seq. #. Gap detected. | Immediately send duplicate ACK, indicating seq. # of next expected byte
Arrival of segment that partially or completely fills gap.|Immediate send ACK, provided that segment starts at lower end of gap
TCP fast retransmit
- TCP fast retransmit
- if sender receives 3 ACKs for same data (“triple duplicate ACKs”), resend unacked segment with smallest seq #
- likely that unacked segment lost, so don’t wait for timeout

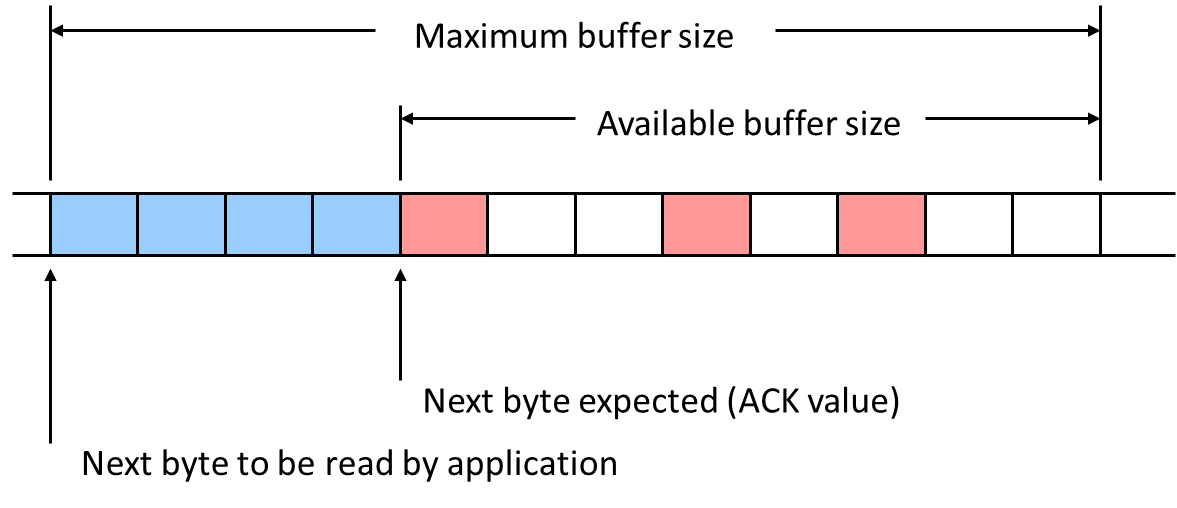
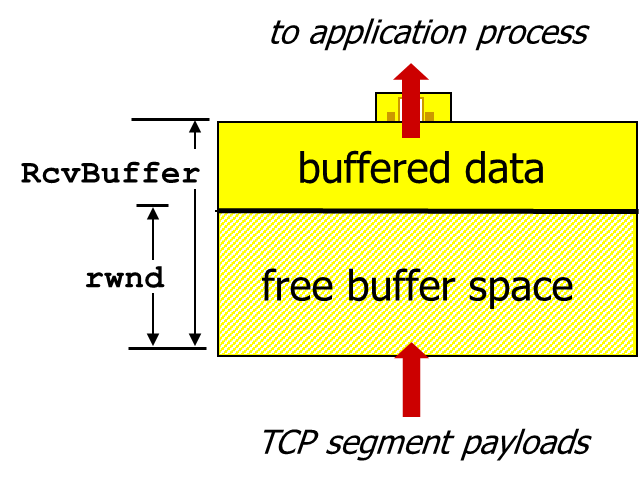
TCP flow control
- flow control
- receiver controls sender, so sender won’t overflow receiver’s buffer by transmitting too much, too fast
- receiver “advertises” free buffer space by including rwnd value in TCP header of receiver-to-sender segments
- sender limits amount of unacked (“in-flight”) data to receiver’s rwnd value
- guarantees receive buffer will not overflow
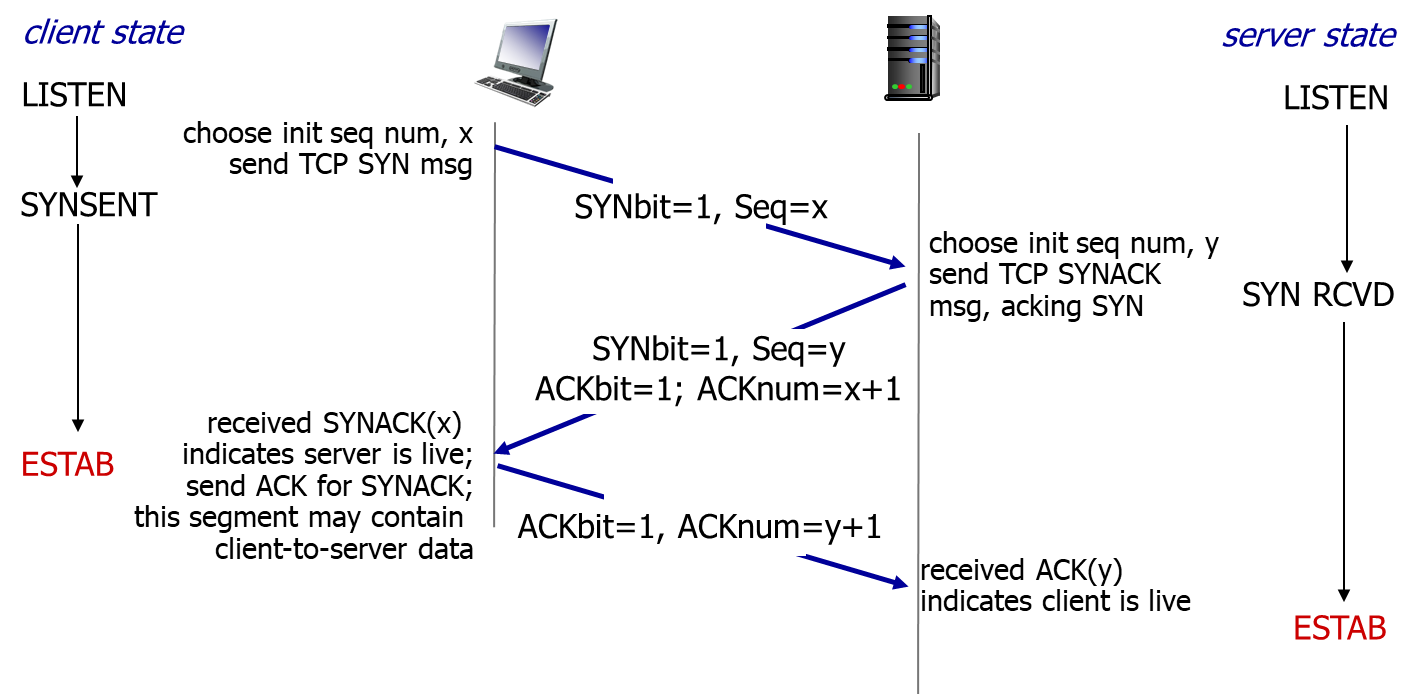
Connection Management
before exchanging data, sender/receiver “handshake”:
- agree to establish connection (each knowing the other willing to establish connection)
- agree on connection parameters
TCP 3-way handshake
TCP closing a connection

Communication Networks (11)
https://yzzzf.xyz/2024/03/06/communication-networks-11/