Communication Networks (3)
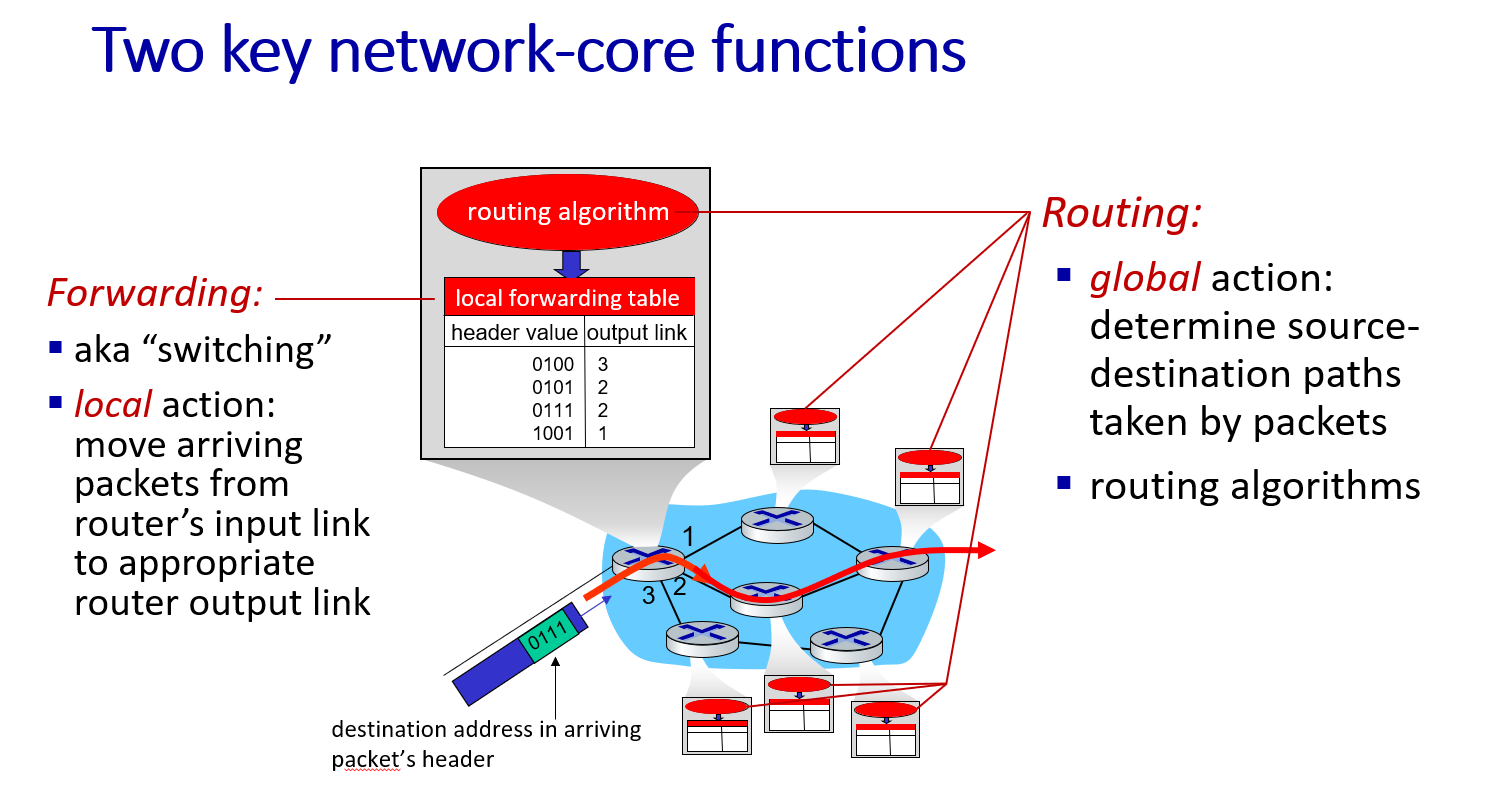
Network-core
2 key functions:
- routing: determine source-destination paths taken by packets
- forwarding (switching): move arriving packets from router’s input link to appropriate router output link
Packet-switching: Store-and-Forward
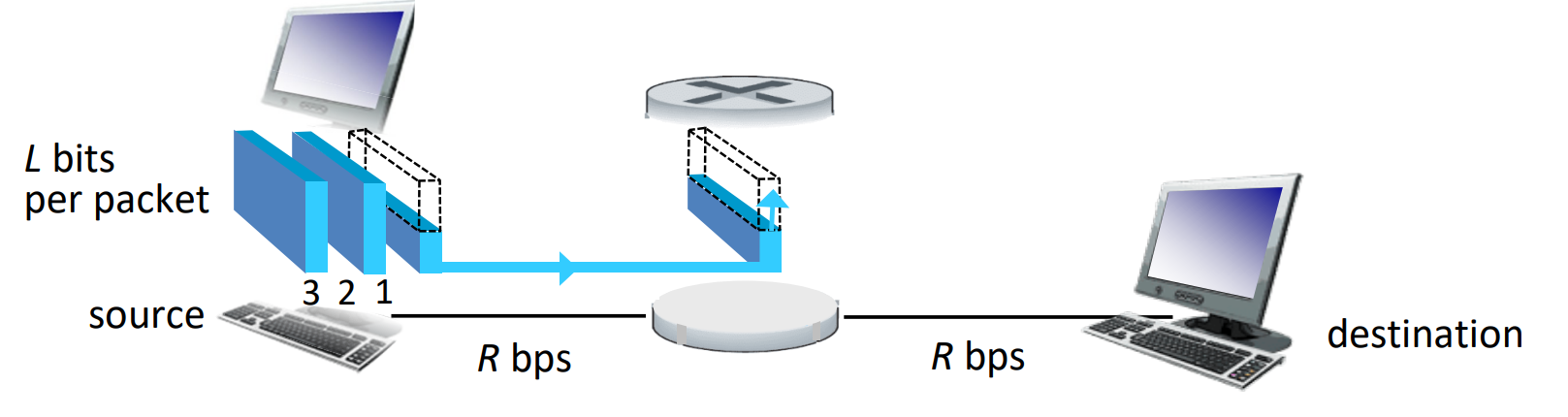
- entire packet must arrive at router before it can be transmitted on next link
- end-end delay = (assuming zero propagation delay)
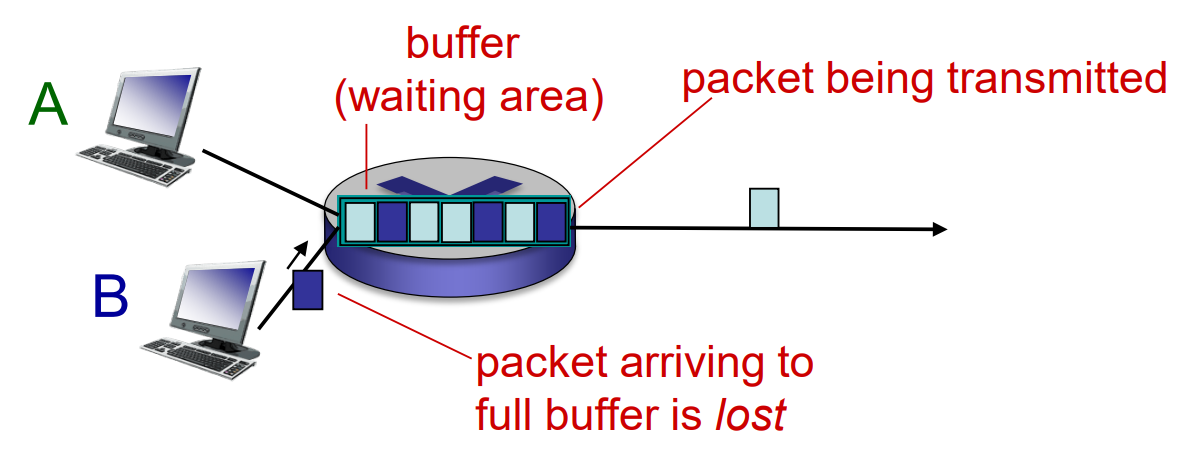
Packet Switching: Queueing Delay, Loss

- if arrival rate > transmission rate,
- packets will queue
- packets can be dropped (lost) if memory (buffer) fills up
Alternative core: Circuit Switching
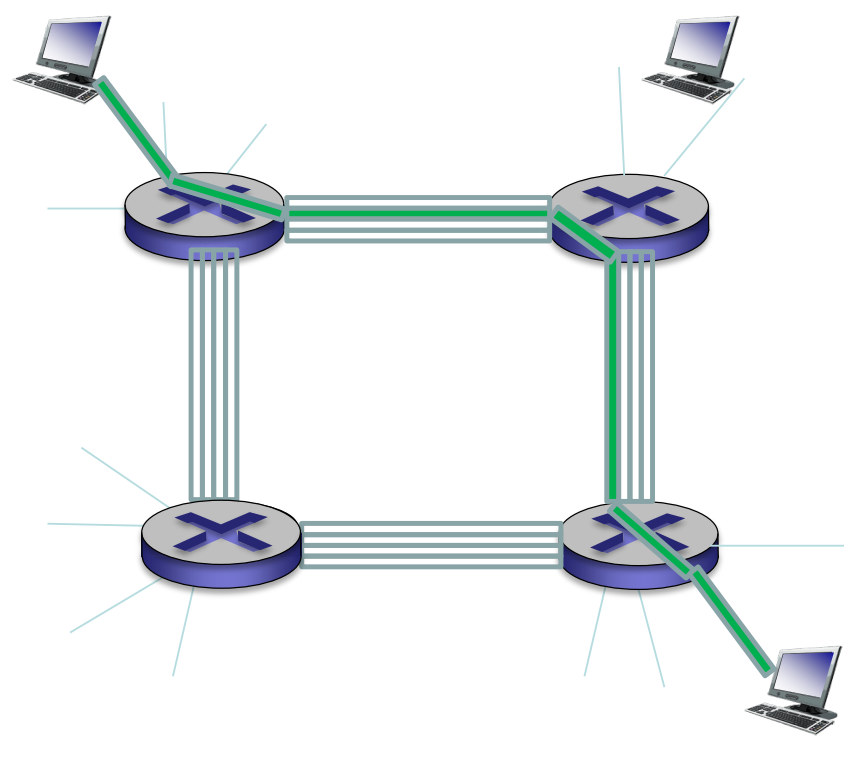
- FDM: Frequency Division Multiplexing
- TDM: Time Division Multiplexing
Internet Structure: Network of Networks
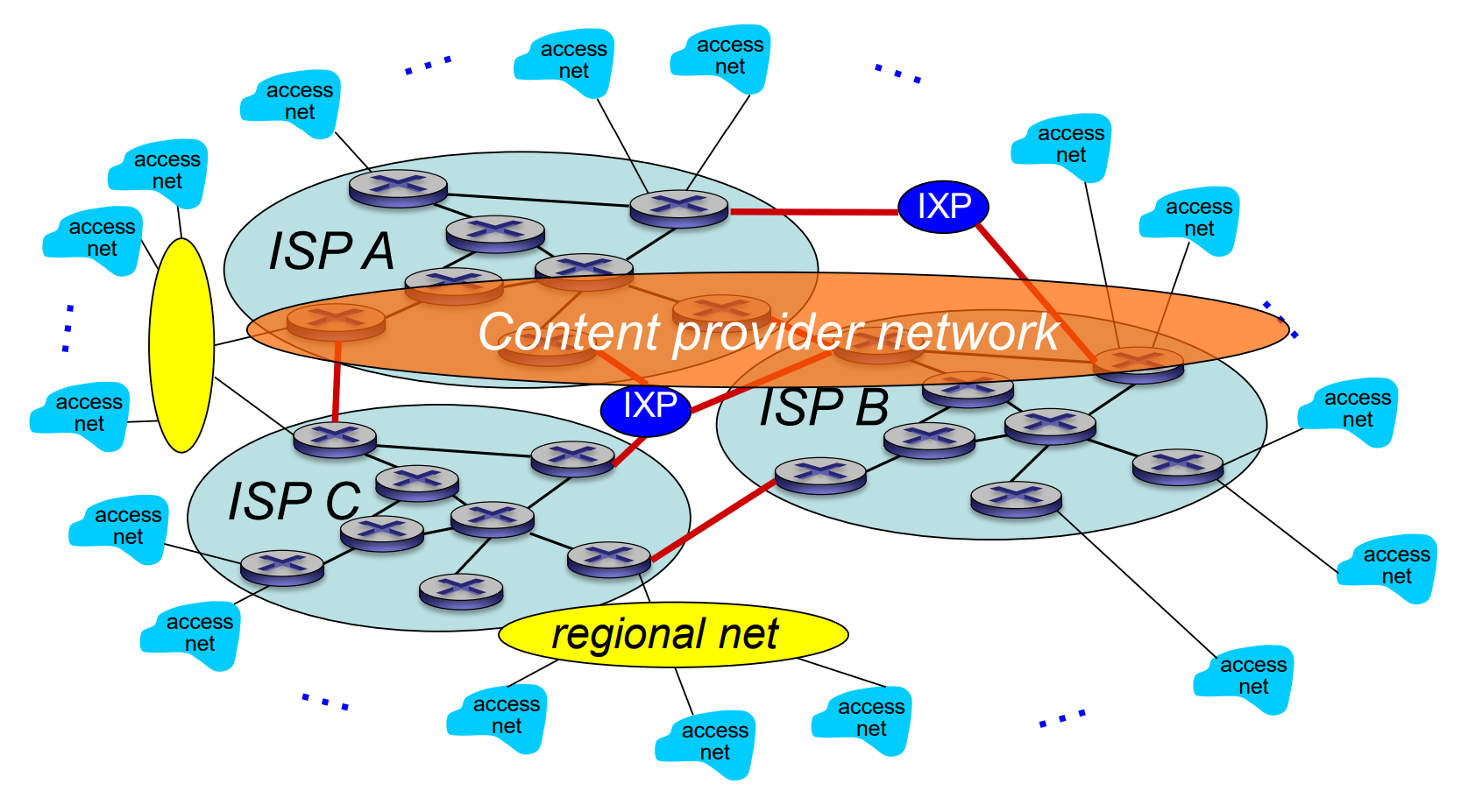
- IXP: Internet exchange point
Delay, Loss, Throughput in networks
-
packet arrival rate to link (temporarily) exceeds output link capacity
-
packets queue, wait for turn
-
packet being transmitted (delay)
-
packets queueing (delay)
-
free (available) buffers: arriving packets dropped (loss) if no free buffers
Delay

- nodal processing delay < msec
- check bit errors
- determine output link
- queueing delay
- time waiting at output link for transmission
- : link bandwidth (bps)
- : packet length (bits)
- : average packet arrival rate
- : avg delay small
- : avg delay large
- : avg delay infinite
- transmission delay
- time to upload bits
- : packet length (bits)
- : link bandwidth (bps)
- propagation delay:
- time to propagate bits from A to B
- : length of physical link
- : propagation speed
Loss
Throughput
- throughput: rate (bits/time unit) at which bits transferred.
- bottleneck link: link on end-end path that constrains end-end throughput
Internet protocol stack
| layer | use |
|---|---|
| application | supporting network applications (FTP, SMTP, HTTP) |
| transport | process-process data transfer (TCP, UDP) |
| network | routing of packets from source to destination (IP, routing protocols) |
| link | data transfer between neighboring network elements (Ethernet, 802.11 (WiFi), PPP) |
| physical | bits on the wire |
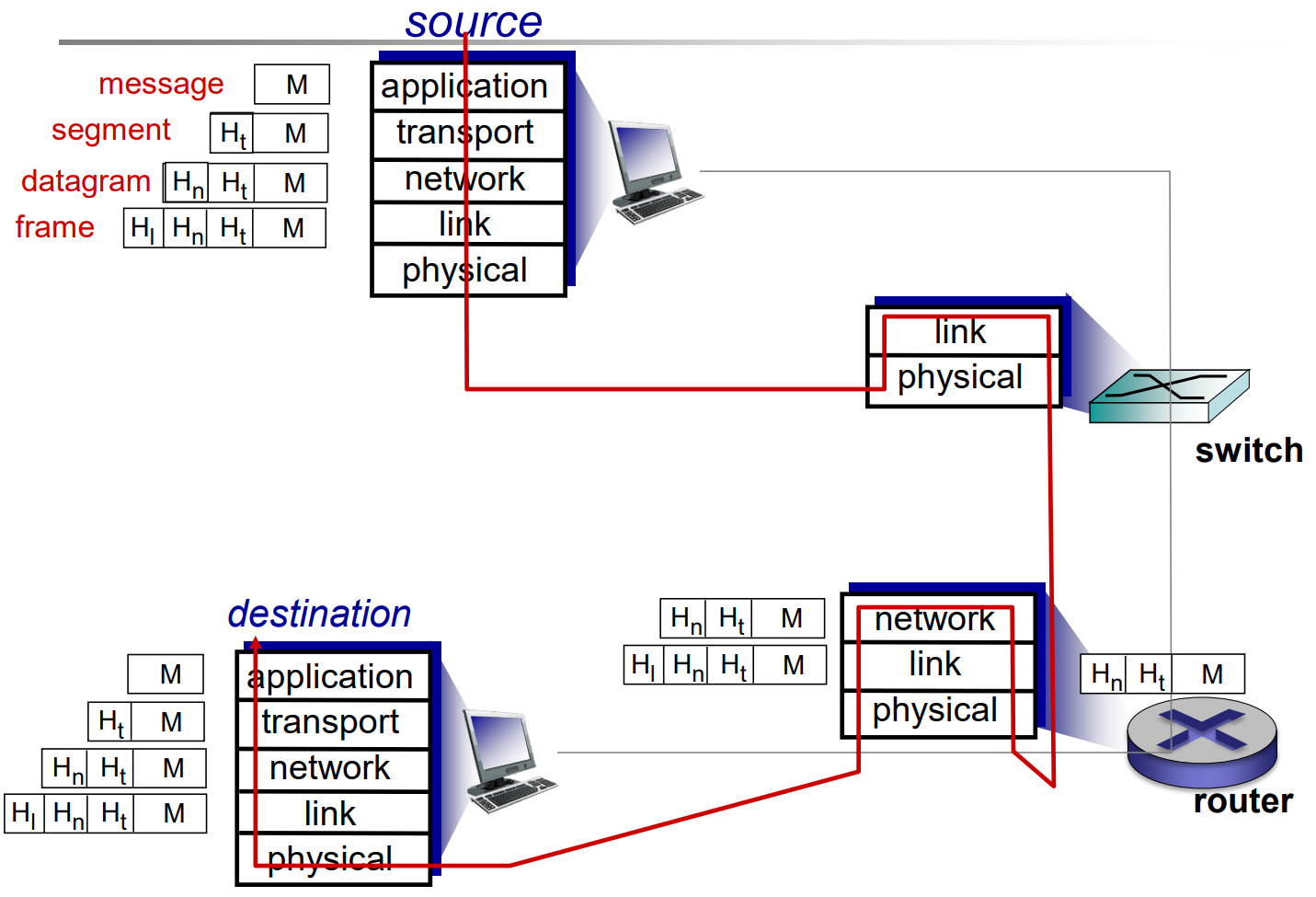
- Switch
- level 2 device
- connects devices on a computer network by using packet switching to receive and forward data to the destination device.
- Router
- level 3 device
- Routers perform the traffic directing functions between networks and on the global Internet.
Communication Networks (3)
https://yzzzf.xyz/2024/01/29/communication-networks-3/