Communication Networks (1-2)
https://birkhoffg.github.io/blog/posts/networking-what-is-networking/
Internet
Internet: “network of networks”
- Interconnected ISPs
Protocols control sending,receiving of messages
- e.g., TCP, IP, HTTP, Skype, 802.11 (WiFi)
Internet standards
- RFC: Request for comments
- IETF: Internet Engineering Task Force
- ISO, IEEE
Internet Structure
Network edge:
- hosts: clients and servers
- servers often in data centers
- access networks, physical media: wired, wireless
communication links
Network core:
- interconnected routers
- network of networks
Connect end systems to edge routers
- residential access nets
- institutional access networks (school, company)
- mobile access networks
- shared or dedicated?
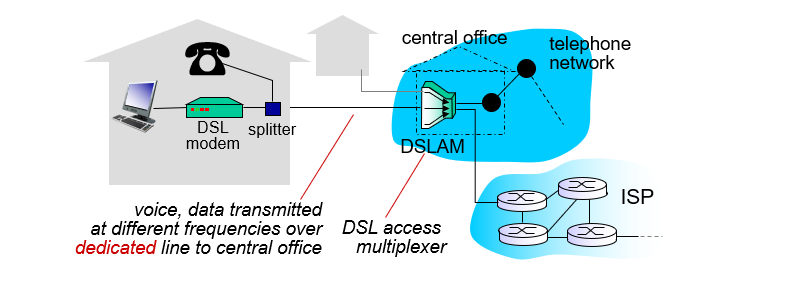
Access Network: Digital Subscriber Line (DSL)
 =
=
- Use existing telephone line to central office DSLAM.
- dedicated access to central office
- < 2.5 Mbps upstream transmission rate (typically < 1 Mbps)
- < 24 Mbps downstream transmission rate (typically < 10 Mbps)
Access Network: Cable Network
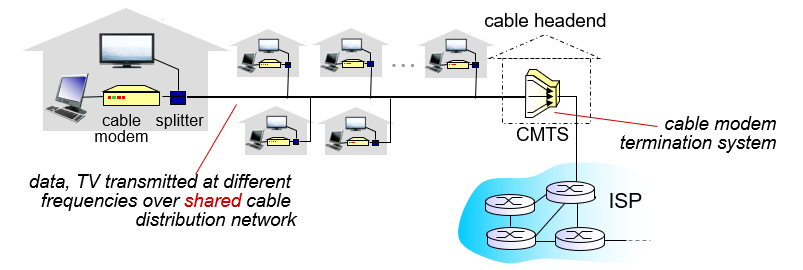
- Frequency division multiplexing: different channels transmitted in different frequency bands
- HFC: hybrid fiber coax up to 30Mbps
- Network of cable, fiber attaches homes to ISProuter
- homes share network to cable headend
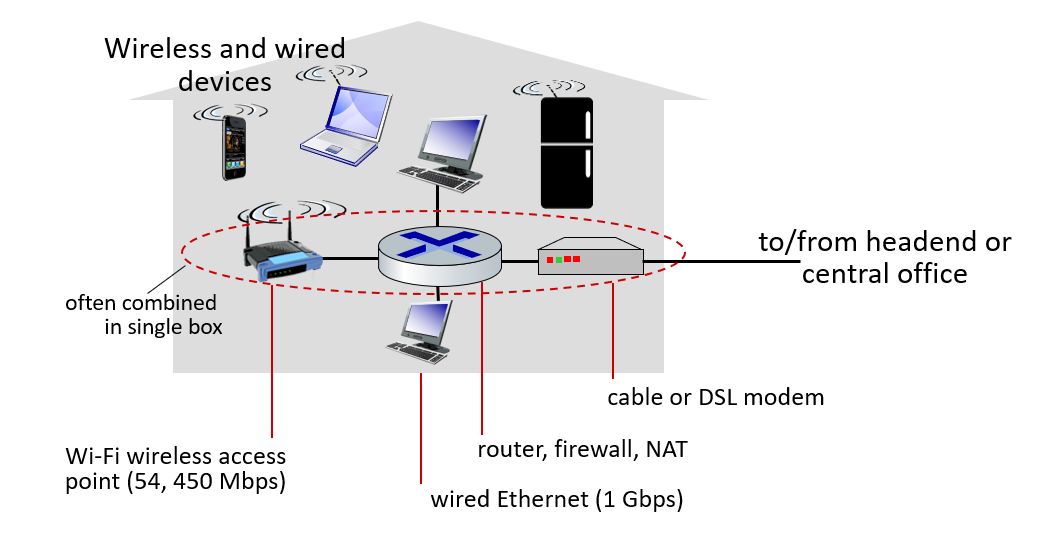
Access Network: Home Network
Enterprise Access Networks (Ethernet)
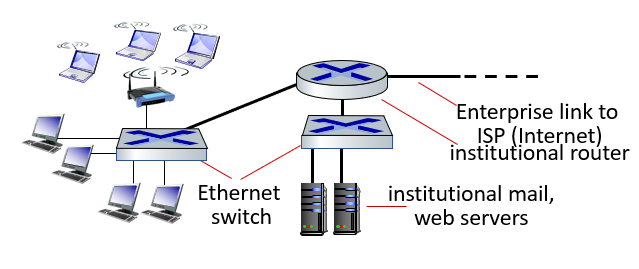
- 10 Mbps,100Mbps,1Gbps, 10Gbps transmission rates
- Today, end systems typically connect into Ethernet switch
Wireless Access Networks
- Shared wireless access to base station aka “access point”
Wireless LANs (WiFi):
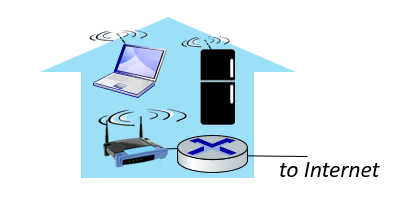
- 11, 54, 450 Mbps rate
Wide-area wireless accesss
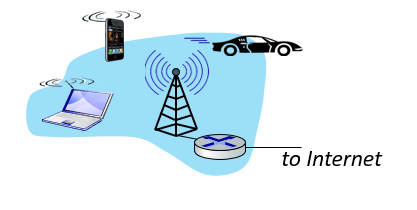
- cellular operator, 10’s km
- 1 to 10 Mbps
- 3G, 4G, LTE
Host: Sends Packets of Data
Host sending function:
- breaks appilication layer messages into smaller chunks (packets), of length bits
- transmits packet into access network at transmission rate
- link transmission rate / link capacity / link bandwidth:
Physical Media
guided media:
- signals propagate in solid media: copper,fiber,coax
unguided media:
- signals propagate freely
e.g., radio
twisted pair (TP):
- two insulated copper Wires
- Category 5:100 Mbps1,Gbps Ethernet / Category 6: 10Gbps
Coaxial Cable:
- multiple channels
Fiber optic cable:
- high-speed point-to-point transmission (e.g.,10’s-100’s Gbps transmission rate)
Network-core
2 key functions:
- routing
- forwarding
Communication Networks (1-2)
https://yzzzf.xyz/2024/01/29/communication-networks-1-2/